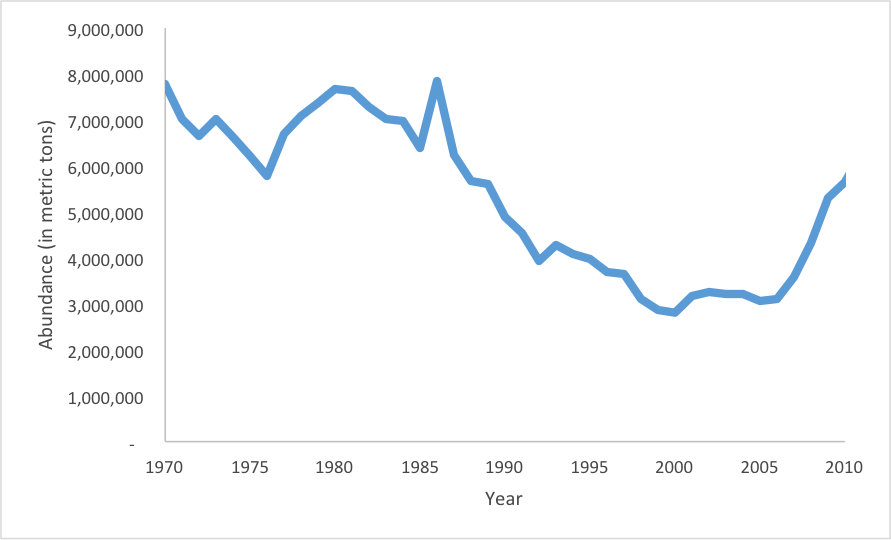
November 1, 2016 — Atlantic cod have been emblematic of fisheries problems, with the 1992 collapse of the Northern cod stock in Canada setting the stage for the last 25 years of concern surrounding status of cod stocks. Mark Kurlansky’s book “Cod” sold over a million copies, increasing awareness and concern over cod fisheries. Further, the two U.S. cod stocks continue to be at very low abundance; an article in the Houston Press released September of 2011 stated“Atlantic cod has been fished nearly to extinction.” However, over the entire Atlantic Ocean, the abundance of cod is high and increasing (Figure 1).
The purpose of this feature is to clarify the myriad of different claims recently released regarding the current status of Atlantic cod to highlight that not all is doom and gloom, but rather a mixed story of good and bad. In other words, not all stocks are low, failing to recover, and doomed to perish. In fact, what we actually see are three broad categories of stocks: those that are doing poorly, those that are low but rebuilding, and those that are large and doing well. In researching this story, we analyzed abundance data collected by scientific institutions and interviewed a range of scientists who have been involved in cod stock assessment and management over the last 15-35 years. These experts include: Chris Zimmermann, Director of the Institute of Baltic Sea Fisheries with 15 years of experience working on ICES stocks; Coby Needle, Head of the Sea Fisheries Programme at MSS Marine Laboratory in Aberdeen, Scotland and an active member of several ICES working groups for 20 years; Jake Rice, Chief Scientist Emeritus at the Department of Fisheries and Oceans, Canada (DFO) with 35 years of experience in cod stock assessment; Robin Cook, a Senior Research Fellow in the MASTS Population Modelling Group at the University of Strathclyde, Glasgow who has been involved in ICES fisheries science since 1982; and Steve Murawski, a Professor of Biological Oceanography at University of South Florida (USF) with 7 years of experience as a Chief Scientist at the U.S. National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS).
The story of cod is complex; there are many different and unique stocks occupying distinct regions within the Atlantic basin that are subject to environmental factors and political influences that differ based on geographic location. “If you look at the whole picture, you see that there is no consistent whole picture…Every single stock develops differently” says Chris Zimmermann. “Stock dynamics are quite different from area to area, so a big picture is difficult to get a handle on because there isn’t one,” agrees Coby Needle. Further, “they all have very different management histories and scenarios in terms of their status” says Steve Murawski.
Status of Stocks
There are over two dozen cod stocks that are defined as management units, 6 of which are addressed in this feature: 2 on the western side and 4 on the eastern side of the Atlantic basin (see Figure 2). The two U.S. stocks are Georges Bank and Gulf of Maine, and the four European stocks occupy the shelves of Iceland, the Barents Sea, the North Sea, the Celtic Sea, and the Baltic Sea.
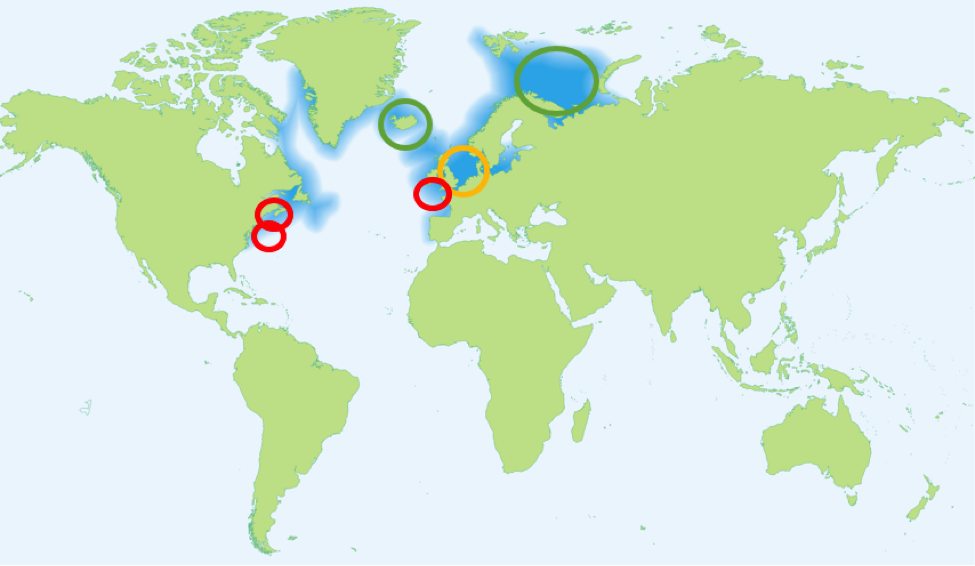 Figure 2. Map showing location of 6 different cod stocks addressed in this feature. The darker blue region represents Atlantic cod distribution, and the 6 circles represent stocks being examined in this feature. Red circles represent stocks that are doing poorly (Celtic Sea, Gulf of Maine, Georges Bank), yellow circles represent stocks that are low but recovering (North Sea), and green circles represent stocks that are doing well (Barents Sea, shelves of Iceland).
Figure 2. Map showing location of 6 different cod stocks addressed in this feature. The darker blue region represents Atlantic cod distribution, and the 6 circles represent stocks being examined in this feature. Red circles represent stocks that are doing poorly (Celtic Sea, Gulf of Maine, Georges Bank), yellow circles represent stocks that are low but recovering (North Sea), and green circles represent stocks that are doing well (Barents Sea, shelves of Iceland).
This feature focuses on the general trends among most of these stocks to demonstrate that rather than all stocks doing poorly, what we actually see are 3 broad categories of stocks: those that are (1) doing poorly, (2) low but rebuilding, and (3) doing well.